Air Pollution Control Management
- At present the purpose of applying and/or developing a control technology is to meet ambient air quality standards and other source related regulations. A control technology can only be applied to a controllable source. Therefore, it will be difficult to think of controlling emissions from a volcano.
- The cost of removing a pollutant from a source generally increases exponentially with the percentage of control. However, this relationship will change if it is possible to recover the pollutant for some economic purposes. For example, the removal of sulfur from gas processing plants was economically feasible in 1960’s because of the high price of sulfur in world market.
- Application of control technology requires knowledge of source, effluents from the source, air pollution regulations and waste generated from the technology. Sometimes it is possible to develop a successful air pollution control technology which leads to the problem of disposing the waste.
- Application of control technology requires knowledge of source, effluents from the source, air pollution regulations and waste generated from the technology. Sometimes it is possible to develop a successful air pollution control technology which leads to the problem of disposing the waste.
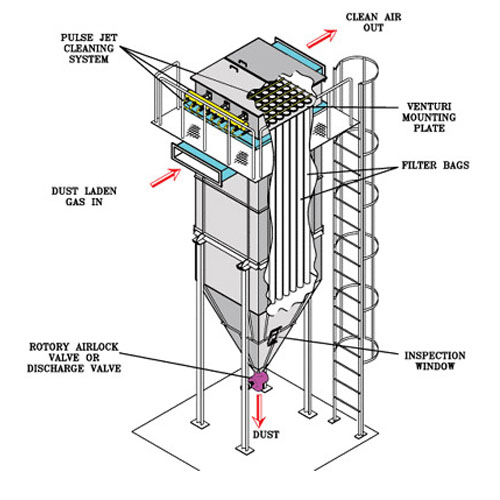
- The techniques for controlling air pollution can be either without an air pollution control device or with air pollution control equipment. The general methods for techniques without an air pollution control device include process change, change in fuel, improve dispersion, good operating practices, and plant shutdown/relocation. Control equipment remove the pollutant, convert to less harmful contaminant or recover a valuable material for further use.